The programming languages used to customize process flows according to the enterprise business and requirements, make extension of the ERP/CRM/SCM interface, functionality, codebase, data manipulation to retrieving, insert, modifications, controls and user experience etc.
+ d365 BC – AL (Application Language)
+ SAP Hana, S/4Hana – ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming – a 4GL object oriented language)
+ Oracle NetSuit – SuiteSript
+ ODOO – Python / XML / JS (opensource ERP)
+ Epicore – BPMs (similar to C#)
+ SalesForce – Apex
+ Zoho – Deluge
+ d365 Finance and Operations – X++ (C# and SQL)
DevOps to ERP Implementation
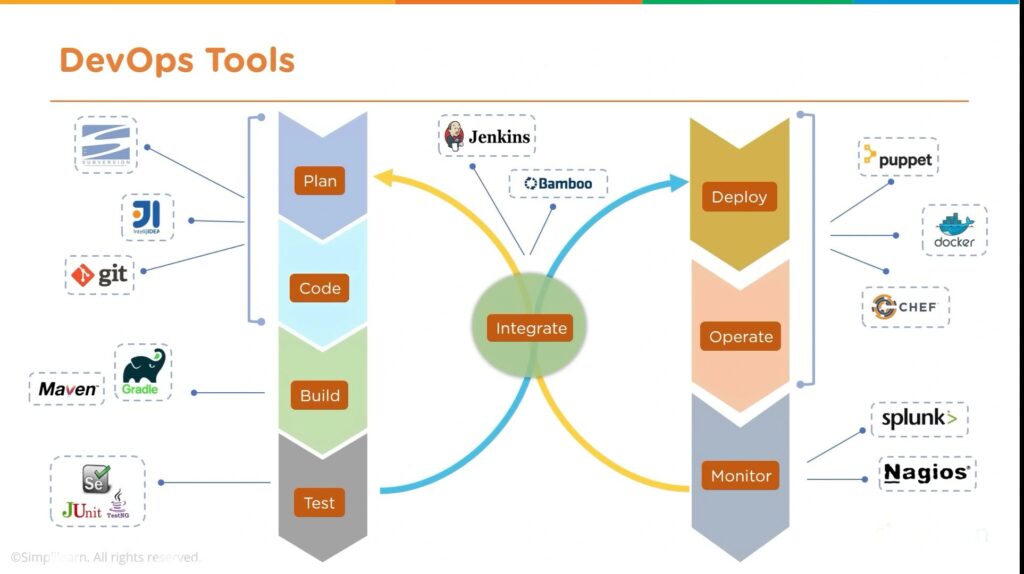
WaterFall project management is historical. Agile with its derivatives – Scrum, Kanban are prevailing but DevOps is the evolution of Agile project management. DevOps – software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) shorten the systems development life cycle and provide continuous delivery with high software quality. ERP implementation is a complex, time-consuming and challenging process that involves the integration of multiple business processes and systems. DevOps helps to streamline and improve the implementation process.
Benefits of using DevOps in ERP implementation:
Reduced time to market:
DevOps reduces the time it takes to implement an ERP system by automating manual tasks and streamlining the development and deployment process. It improves the quality of the ERP implementation by automating testing and continuous integration
Increased agility:
Making the organizations to be more agile and responsive to change. This is important for ERP implementations, which can often change scope and requirements over time. Automating tasks and improving efficiency ensures cost reduction.
Some specific ways to use DevOps in ERP implementation:
Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline: Used to automate the build, test, and deployment process, which reduces the time it takes to deploy changes to the ERP system and improve the quality of the deployment process.
Use infrastructure as code:
Infrastructure as code allows to define the infrastructure in code. This helps to automate the provisioning and configuration of your ERP environment, which reduces the time it takes to set up and deploy your ERP system.
Use cloud computing:
Cloud computing provides a scalable and flexible platform for ERP implementation. This helps to reduce the costs of ERP implementation and make it easier to deploy and manage your ERP system. DevOps is more than just a set of tools and practices. It is also a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement to create a more efficient and effective ERP implementation process.
Here are some additional tips for using DevOps in ERP implementation. Starting small Don’t try to implement DevOps across your entire ERP implementation at once. Getting buy-in from all stakeholders is crucial. DevOps is a team effort. It is important to get buy-in from all stakeholders, including business users, IT operations, and development teams.
Use the right tools and technologies: There are a number of tools and technologies that can help to implement DevOps in ERP implementation. Choose the tools and technologies that are right for your organization and your ERP system. DevOps can be a valuable tool for ERP implementation. By adopting DevOps practices, you can reduce the time to market, improve the quality of your ERP implementation, increase your agility, and reduce costs.
Audit Trail of SaaS (ERP) usage in the Cloud
Creating and maintaining an audit trail for an ERP system in the cloud is crucial for tracking and monitoring all activities within the system. Here are some steps to establish an audit trail:
* Enable Audit Logging:
Most modern ERP systems and cloud platforms offer built-in audit logging capabilities. Enable these features to start recording activities.
* Define Audit Policies:
Determine what activities you want to track and log. Common events to audit include user logins, data changes, configuration modifications, and access to sensitive data.
* Capture User Activities:
Record who performed each action, including their username and IP address. This information is critical for identifying unauthorized access or suspicious behavior.
* Data Changes:
Track changes to critical data fields, such as financial transactions, employee records, and inventory levels. Capture the old and new values to facilitate forensic analysis.
* Timestamps:
Include timestamps for each logged event to establish a timeline of actions within the ERP system.
* Data Retention:
Define a data retention policy for audit logs. Ensure that logs are stored securely and comply with any regulatory requirements for data retention.
* Access Controls:
Limit access to audit logs to authorized personnel only. Implement role-based access controls to restrict who can view and manage the logs.
* Encryption:
Consider encrypting audit logs both in transit and at rest to protect them from unauthorized access.
* Regular Review:
Schedule regular reviews of audit logs to detect anomalies or suspicious activities. Automated alerting can help notify administrators of potential issues in real-time.
* Reporting:
Generate reports from audit logs to provide insights into system usage and security. These reports can be useful for compliance reporting and investigations.
* Integration:
Integrate your audit trail with a centralized security information and event management (SIEM) system for comprehensive monitoring and analysis.
* Archiving and Backups:
Ensure that audit logs are regularly backed up and archived to prevent data loss and maintain historical records.
* Compliance:
Ensure that your audit trail setup complies with industry-specific regulations and standards, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Act), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), or PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) , if applicable to your organization.
* Response Plan:
Develop an incident response plan that outlines actions to take in case of security incidents or breaches detected through the audit trail.
* Training:
Train the IT and security teams on how to interpret and respond to audit log data effectively.
These steps are very important to establish a robust audit trail for your ERP system in the cloud, enhancing security, compliance, and accountability of the organization
Enterprise Finance and Accounting – Cloud Hosting
Finance and accounting organizations have several compelling reasons to host their applications in the cloud:
1. Cost Efficiency: Cloud hosting eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure, reducing hardware and maintenance costs. Organizations can scale resources up or down as needed, paying only for what they use.
2. Accessibility: Cloud-based applications can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration. This flexibility is especially important for finance and accounting professionals who may need to work from various locations.
3. Scalability: Cloud platforms offer the ability to easily scale computing resources to accommodate fluctuating workloads, such as during tax season or financial audits.
4. Security: Many cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and regular updates, which can be more robust than what individual organizations can afford to implement.
5. Disaster Recovery: Cloud providers often have robust disaster recovery and backup solutions, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or natural disasters.
6. Collaboration: Cloud-hosted applications facilitate real-time collaboration among team members, allowing for streamlined financial reporting and data sharing.
7. Compliance: Cloud providers may offer compliance certifications and tools to help organizations meet industry-specific regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, which are critical for finance and accounting data.
8. Integration: Cloud platforms often provide APIs and integration capabilities that make it easier to connect accounting and finance applications with other business systems, improving workflow efficiency.
9. Automatic Updates: Cloud applications typically receive regular updates and patches, ensuring that organizations have access to the latest features and security enhancements.
10. Data Analytics: Cloud-based platforms can leverage advanced analytics and machine learning tools to gain insights from financial data, helping organizations make more informed decisions.
In summary, hosting finance and accounting applications in the cloud offers cost savings, flexibility, security, and scalability, while also enabling collaboration and compliance with industry regulations. These benefits make cloud hosting an attractive option for organizations in this sector.
